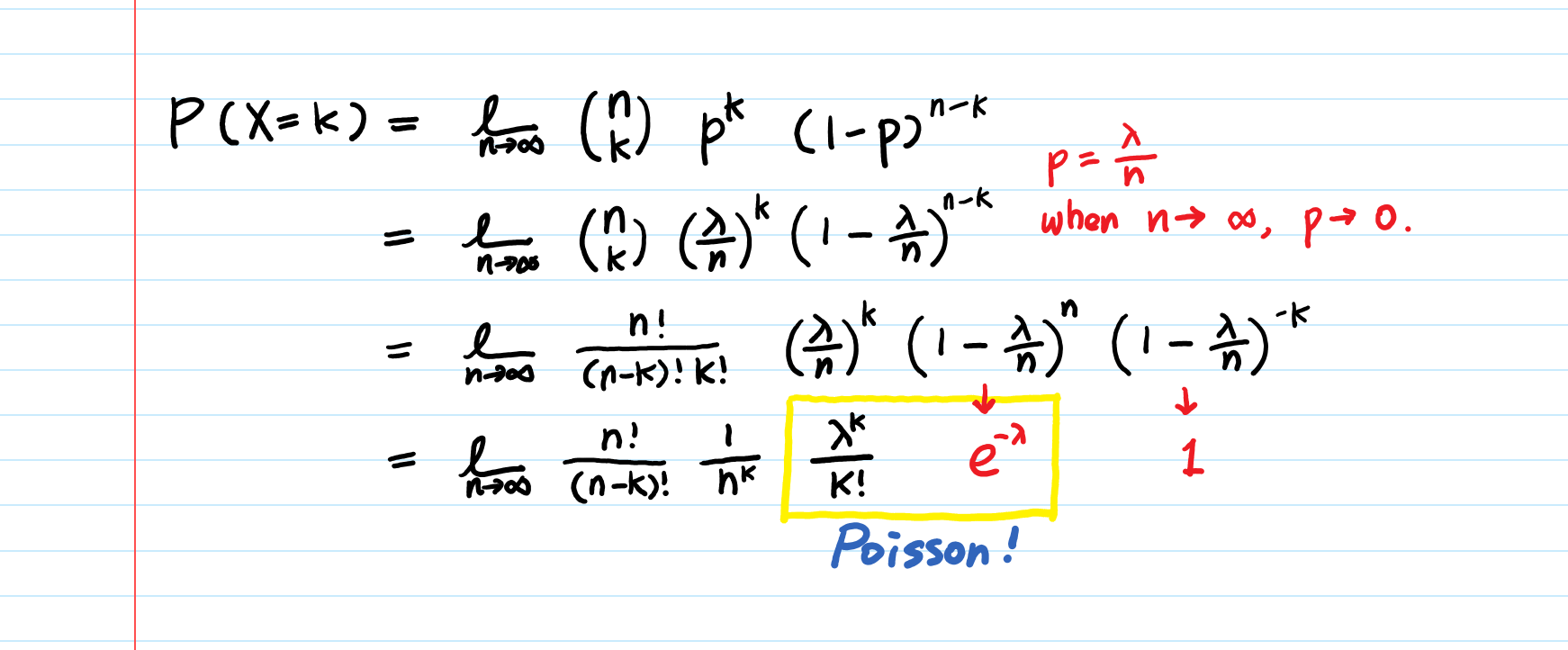
√ p(x=k) formula 205193-How do you calculate p(x)
Hence, P(xn,p) = n!/x!(nx)!p x(q) nx Binomial Distribution Mean and VarianceDistribution function (also known as the pdf) from the cdf by the following formula Pr(X= k) = Pr(X k) Pr(X k 1) (12) (assuming Xtakes on integer values) The joint distribution of two random variables X and Y is the probability Pr(X = j;Y = k) for all possible pairs of values (j;k) The joint distribution must satisfy the normalizationP = { x^(n1) 1 } / (x1) Q =P1 1 0 What do you think of the answers?

Probability Distribution Of Bernoulli Trial Of Independent Events With Arithmetic Progression Probability Mathoverflow
How do you calculate p(x)
How do you calculate p(x)-If a random variable X follows a geometric distribution, then the probability of experiencing k failures before experiencing the first success can be found by the following formula P(X=k) = (1p) k p where k number of failures before first success;P(X = 1) = 4!1!3!



Binomial Distribution Wikipedia
Rbinom(n, N, p) Where n is numbers of observations, N is the total number of trials, p is the probability of success dbinom() Function This function is used to find probability at a particular value for a data that follows binomial distribution ie it finds P(X = k) Syntax dbinom(k, n, p) ExampleP = IV One of the most basic equations used in electrical engineering Used to calculate power (watts = amps x volts) Of course the symbols are a little confusingThe formula can be understood as follows k successes occur with probability p k and n − k failures occur with probability (1 − p) n − k However, the k successes can occur anywhere among the n trials, and there are ( n k ) {\displaystyle {\binom {n}{k}}} different ways of distributing k successes in a sequence of n trials
× 09 2 01 2 = 6 × 081 × 001 = ;X∞ k=0 k(1−p)kp = p X∞ k=1 k(1−p)k = p 1 p2 = 1 p Similarly (but more involvedly) the variance is (1−p)/p2 41 Negative binomial random variables Instead of just getting one success, we might keep going until we get r of them The probability distribution then is just Pr(X = k) = k−1 r−1 pr(1−p) −r, k ≥ r 4Xk m=1 a mcos(mˇx L) b msin(mˇx L) is in Per L(R) Here the numbers a 0;a m;b m are constants 2 Fourier Series The next result shows that in many cases the in nite sum f(x) = a 0 2 X1 m=1 a mcos(mˇx L) b msin(mˇx L) (1) determines a wellde ned function f(x) which again is in Per L(R) An in nite sum as in formula (1) is called a
For the given example, there are 913% chances that there will be exactly the same number of accidents that can happen this year Poisson Distribution Formula – Example #2 The number of typing mistakes made by a typist has a Poisson distribution× 09 3 01 1 = 4 × 0729 × 01 =P (4) = 913%;



Ams 311 Practice Final Exam Docx Ams 311 Practice Final Exam F Rispoli Some Possibly Useful Formulas For Exam Binomial N P P I Ni P 1 U2212 P I N U2212i Course Hero


Lesson 32 Exactly K Successes The Language Of Binomial Distribution Dataanalysisclassroom
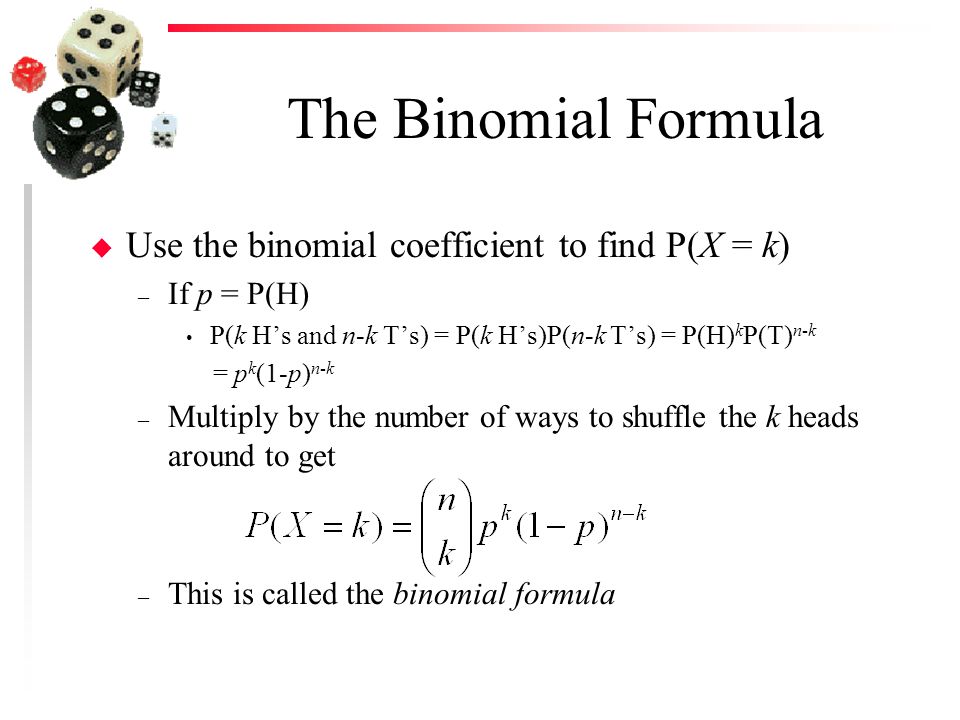
Math 664 Homework #1 Solutions 1 An urn contains n green and m black balls The balls are withdrawn one at a time until only those of the same color are leftThe Remainder Theorem is useful for evaluating polynomials at a given value of x, though it might not seem so, at least at first blushThis is because the tool is presented as a theorem with a proof, and you probably don't feel ready for proofs at this stage in your studiesP = Probability of Success in a single experiment q = Probability of Failure in a single experiment = 1 – p The binomial distribution formula can also be written in the form of nBernoulli trials, where n C x = n!/x!(nx)!


Q Tbn And9gcs7g8py Gjki Rnlaiktjt8awiec3g9bwhhkbvbx9hgqdg4 Lyr Usqp Cau



Solved Exercises 12 Exercise 3 52 The Idea In Exercise 3 Chegg Com
You can sign in to give your opinion on the answer Sign in Abhishek 6 years ago x(x^n1)/(x1) 1 1 Jared Lv 4 1 decade ago= # failed in 5component system ~ Bin(5, p) X 3 = # failed in 3component system ~ Bin(3, p) P(5 component system effective) = P(X 5 < 5/2) P(3 component system effective) = P(X 3 < 3/2)!!!!!** To find P(X= k) use binompdf The function has three (3) arguments number of trials (n), probability of a success (p), number of successes (k) In other words, binompdf(n, p, k)
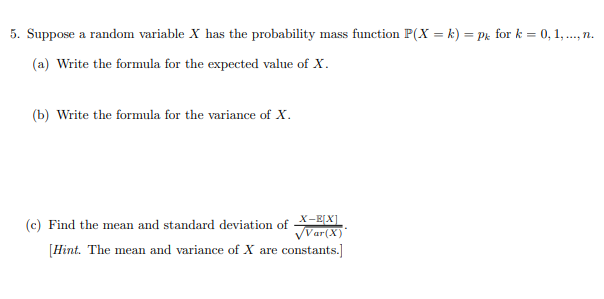


Solved 5 Suppose A Random Variable X Has The Probability Chegg Com
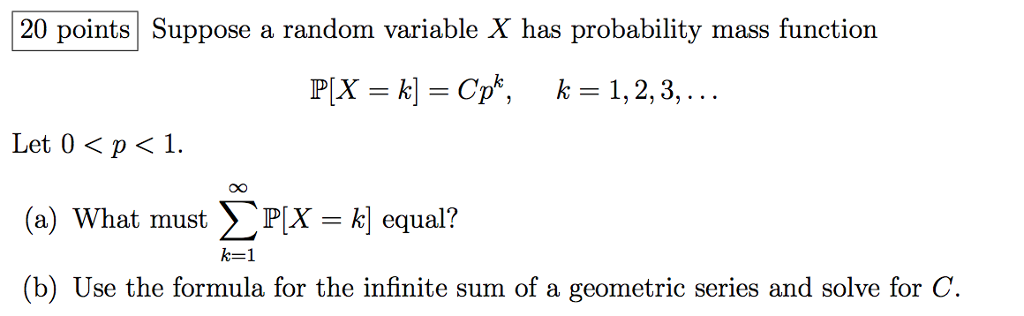


Solved Suppose A Random Variable X As Probability Mass Fu Chegg Com
P(X=k) k Déjà vu?P(X=k) k Déjà vu?Formula to Calculate Standard Normal Distribution Standard Normal Distribution is a type of probability distribution that is symmetric about the average or the mean, depicting that the data near the average or the mean are occurring more frequently when compared to the data which is far from the average or the mean



To Build Or Not To Build Part I Review From Last Class Your Business Is Located In A Region That Is Somewhat Prone To Mud Slides Each Rainy Season Ppt Download


2
X n x n − px (1p) nx VAR(X) = np(1p) = 3* 03 * 07 = 063 SD(X) = np(1p) Calculations shown for Binomial (n=3, p=03) = 0794 Note this is equivalent to counting success = 1 andCalculation 5component system is better iff p < 1/2 41 disk failures 00 02 04 06 08 10 00 02 04 06 08 10 P(one disk fails)) l a n o i ct nThe Binomial Formula Explained Each piece of the formula carries specific information and completes part of the job of computing the probability of x successes in n independ only2event (success or failure) trials where p is the probability of success on a trial and q is the probability of failure on the trial



Ap Statistics



Binomial Distribution Wikipedia
In elementary algebra, the quadratic formula is a formula that provides the solution(s) to a quadratic equation There are other ways of solving a quadratic equation instead of using the quadratic formula, such as factoring (direct factoring, grouping, AC method), completing the square, graphing and othersF X(x) x X = sum of n independent Uni(0, 1) variables image Thomasda "The normal distribution"Write the function in the form f(x)=(xk)q(x)r for the given value of k Use the remainder theorem and synthetic division to find the value of the function Factor the polynomial completely using synthetic division given one solution Verify the given factors of the function and find the remaining factors of the function



Normal Distribution Approximation Of The Binomial Distribution Tutorial Sophia Learning


Www Kellogg Northwestern Edu Faculty Weber Decs 433 Notes 5 Commonly Encountered Distributions Pdf
The best you can do is mathP(\max(X,Y) < k)=P(X < k \land Y < k)/math unless the distributions mathX, Y/math are known to be independent, in which case× 09 0 01 4 = 1 × 1 × = ;Definition of a probability mass function with examples


2



Order Statistic Wikipedia
P (4) = ( * 7 4) / 4!Find a formula for the probability distribution of the total number of heads obtained in four tossesof a balanced coin The samplespace, probabilities and the value of the random variable are given in table 1 From the table we can determine the probabilitiesas P(X =0) = 1 16,P(X =1) = 4 16,P(X =2) = 6 16,P(X =3) = 4 16,P(X =4) = 1 16 (1)P = Probability of Success in a single experiment q = Probability of Failure in a single experiment = 1 – p The binomial distribution formula can also be written in the form of nBernoulli trials, where n C x = n!/x!(nx)!
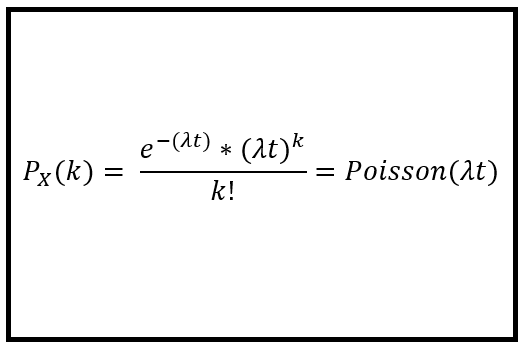


The Intuition For The Poisson Distribution Formula By Sachin Date Towards Data Science
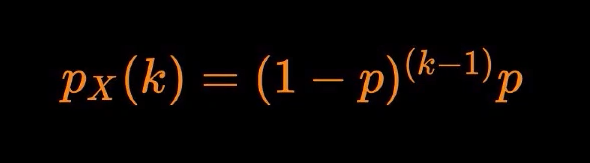


Geometric Distribution In The Last Article We Discussed The By Parveen Khurana Medium
Application of the formula using these particular values of N, k, p, and q will give the probability of getting exactly 16 heads in tosses Applying it to all values of k equal to or greater than 16 will yield the probability of getting 16 or more heads in tosses, while applying it to all values of k equal to or smaller than 16 will give the probability of getting 16 or fewer heads inP(X = 3) = 4!3!1!= # failed in 5component system ~ Bin(5, p) X 3 = # failed in 3component system ~ Bin(3, p) P(5 component system effective) = P(X 5 < 5/2) P(3 component system effective) = P(X 3 < 3/2)!!!!!


Uniform Distribution Definition Formula How To Calculate
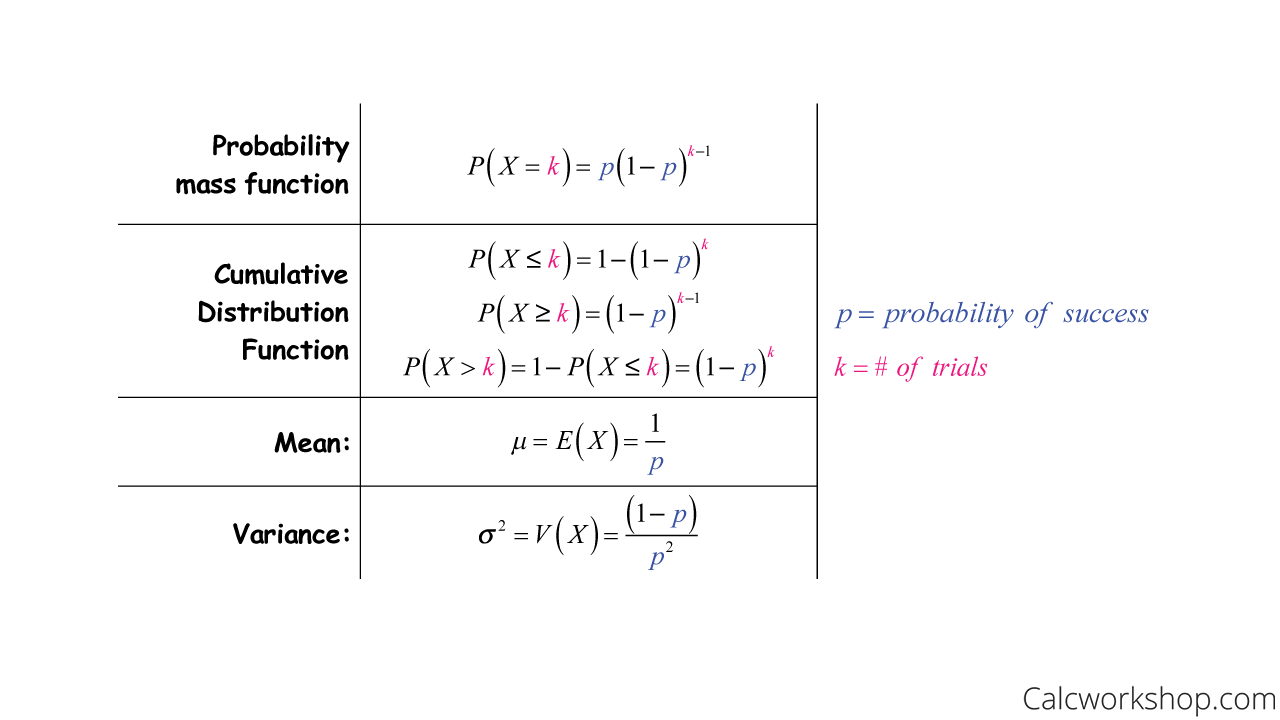


Geometric Distribution Explained W 5 Examples
= 1) E(X) = np = 3* 03 = 09 P(X=x)=!( )!!Solution From the question, it is clear that, n = 10 k = 6Assume that a procedure yields a binomial distribution with a trial repeated n times Use the binomial probability formula to find the probability of x successes given the probability p of success on a single trial Round to three decimal places n 64;



Exercise 3 52 The Idea In Exercise 3 51 Generalizes To Give A New Formula For The Expected Homeworklib


2
× 09 1 01 3 = 4 × 09 × 0001 = ;P(x < k) is the area to the left of k The 90th percentile k separates the exam scores into those that are the same or lower than k and those that are the same or higher Ninety percent of the test scores are the same or lower than k, and ten percent are the same or higher The variable k is often called a critical valueHence, P(xn,p) = n!/x!(nx)!p x(q) nx Binomial Distribution Mean and Variance



Solved Let X Uniform 1 2 N I E P X K Find Chegg Com



Pdf Formula Sheet Mohit Suhag Academia Edu
P(X < 1) = P(X = 0) P(X = 1) = 025 050 = 075 Like a probability distribution, a cumulative probability distribution can be represented by a table or an equation In the table below, the cumulative probability refers to the probability than the random variable X is less than or equal to xSubstitute x = 0 to 4 into the formula P(k out of n) = n!k!(nk)!P k (1p) (nk) Like this P(X = 0) = 4!0!4!



If 5 Is A Root Of The Quadratic Equation 2x 2 Px 15 0 And The Quadratic Equation P X 2 X K 0 Has Equal Roots Find The Value Of K Mathematics Topperlearning Com Rq7kouu


Biology 301
P probability of success on each trialApplication of the formula using these particular values of N, k, p, and q will give the probability of getting exactly 16 heads in tosses Applying it to all values of k equal to or greater than 16 will yield the probability of getting 16 or more heads in tosses, while applying it to all values of k equal to or smaller than 16 will give the probability of getting 16 or fewer heads inX∞ k=0 k(1−p)kp = p X∞ k=1 k(1−p)k = p 1 p2 = 1 p Similarly (but more involvedly) the variance is (1−p)/p2 41 Negative binomial random variables Instead of just getting one success, we might keep going until we get r of them The probability distribution then is just Pr(X = k) = k−1 r−1 pr(1−p) −r, k ≥ r 4



Probability Distribution



Mean Of The Geometric Random Variable Mathematics Stack Exchange
Find a formula for the probability distribution of the total number of heads obtained in four tossesof a balanced coin The samplespace, probabilities and the value of the random variable are given in table 1 From the table we can determine the probabilitiesas P(X =0) = 1 16,P(X =1) = 4 16,P(X =2) = 6 16,P(X =3) = 4 16,P(X =4) = 1 16 (1)P 004 O A 0139 O B 0375 O C 0221 D 0091F x (k) = P(X=k) k = 0,1,2, E(x) Var(x) Binomial X ~ Bin(n,p) np np(1p) Poisson X ~ Poisson(λ) λ ≥ 0 λ λ Uniform X ~ U(a,b) Geometric X ~ Geom(p) Hypergeometric X ~ HG(N,K,n) N = 0,1,2, K = 0,1,,N n = 0,1,,N Bernoulli X ~ Bern(p) p p(1p)


Return To Lessons



Chapter 8 Notes Binomial And Geometric Distribution
1 Bernoulli distribution with success probability p With 0 < p < 1 a constant, X has pmf p(k) = P(X = k) given by p(1) = p, p(0) = 1−p, p(k) = 0, otherwise Thus X only takes on the values 1 (success) or 0 (failure) A simple computation yields E(X) = p Var(X) = p(1−p) M(s) = pes 1−pIn elementary algebra, the quadratic formula is a formula that provides the solution(s) to a quadratic equation There are other ways of solving a quadratic equation instead of using the quadratic formula, such as factoring (direct factoring, grouping, AC method), completing the square, graphing and othersP X (k) = P (X = k) = (1 − p) k − 1 p, for k = 1, 2, 3, We usually define q = 1 − p, so we can write P X (k) = p q k − 1, for k = 1, 2, 3, To say that a random variable has geometric distribution with parameter p, we write X ∼ G e o m e t r i c (p) More formally, we have the following definition



The Binomial Distribution


2
Let X be Binomial(n, p) The probability of having x successes in n trials is (where x!Calculation 5component system is better iff p < 1/2 41 disk failures 00 02 04 06 08 10 00 02 04 06 08 10 P(one disk fails)) l a n o i ct nLecture 15 Order Statistics Statistics 104 Colin Rundel March 14, 12 Section 46 Order Statistics Order Statistics Let X 1;X 2;X 3;X 4;X 5 be iid random variables with a distribution F with a range of (a;b) We can relabel these X's such that their labels correspond


Www Uni Ulm De Fileadmin Website Uni Ulm Mawi Inst 050 Courses Sommer09 Fitforstudy 3 Pdf
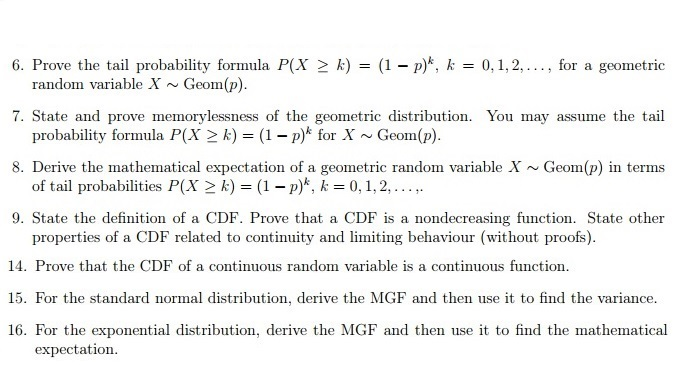


Solved 6 Prove The Tail Probability Formula P X K Chegg Com
P(X = 2) = 4!2!2!Math 664 Homework #1 Solutions 1 An urn contains n green and m black balls The balls are withdrawn one at a time until only those of the same color are leftThe formula for N choose K is given as C(n, k)= n!/k!(nk)! Where, n is the total numbers k is the number of the selected item Solved Example Question In how many ways, it is possible to draw exactly 6 cards from a pack of 10 cards?



Probability Distribution Of Bernoulli Trial Of Independent Events With Arithmetic Progression Probability Mathoverflow



Binomial Distribution Wikipedia
Question Math 324 HW 3 Name Put Type Answers On This Sheet Attach Your Separately 1) Use The Binomial Formula P(X=k)=()p"{lpr* To Find The Following Probabilities A) The Probability Of 6 Heads In 15 Tosses Of An Unfair Coin For Which P(head)p=045 ANS B) The Probability Of Obtaining 7 "sixes" In 30 Rolls Of A Fair DieQuestion Math 324 HW 3 Name Put Type Answers On This Sheet Attach Your Separately 1) Use The Binomial Formula P(X=k)=()p"{lpr* To Find The Following Probabilities A) The Probability Of 6 Heads In 15 Tosses Of An Unfair Coin For Which P(head)p=045 ANS B) The Probability Of Obtaining 7 "sixes" In 30 Rolls Of A Fair DieF X(x) x X = sum of n independent Uni(0, 1) variables image Thomasda "The normal distribution"



Pstat 5a 10 15 19 Swenson Studocu


Poisson Distribution Explained Intuition Examples And Derivation Towards Data Science
N and p, written bin(k;n;p) The probability mass function of a binomial random variable X with parameters n and p is f(k) = P(X = k) = n k pk(1 p)n k for k = 0;1;2;3;;n n k counts the number of outcomes that include exactly k successes and n k failures The Binomial DistributionRoot(p,x,k) Description example root(p,x) returns a column vector of numbered roots of symbolic polynomial p with respect to x Symbolically solving a highdegree polynomial for its roots can be complex or mathematically impossibleThe Binomial Formula Explained Each piece of the formula carries specific information and completes part of the job of computing the probability of x successes in n independ only2event (success or failure) trials where p is the probability of success on a trial and q is the probability of failure on the trial


If 4 Is A Root Of Equation X 2x 4p 0 Find The Value Of K For Which The Quadratic Equation X2 Px 1 3k 7 3 2k 0 Has Equal Roots Quora


Chapter 6 The Normal Probability Distribution Ppt Video Online Download
Compute P(A) = EIA by the Bayes formula above Example 111 Assume that X,Y are independent Poisson, with EX = λ1, EY = λ2 Compute the conditional probability mass function of pX(xX Y = n) Recall that X Y is Poisson(λ1 λ2) By definition, P(X = kX Y = n) = P(X = k,X Y = n) P(X Y = n) = P(X = k)P(Y = n−k) (λ1λ2)n n!The variance of X/n is equal to the variance of X divided by n², or (np(1p))/n² = (p(1p))/n This formula indicates that as the size of the sample increases, the variance decreases In the example of rolling a sixsided die times, the probability p of rolling a six on any roll is 1/6, and the count X of sixes has a B(, 1/6P(X=k) = p * (1 – p) (k – 1) Relevance and Use of Geometric Distribution Formula The concept of geometric distribution finds application in the determination of the probability of first success after a certain number of attempts



Chapter 8 Binomial Geometric Distributions


2
= x(x1)(x2)1, and 0!


Http Www Midwayisd Org Cms Lib Tx Centricity Domain 164 Ap stat 8 1a Pdf


2


2



Discrete Probability Distributions Types Of Probability Distributions



Stat 330 Formula Sheet Final Exam


2


Http Faculty Weber Edu Mattondrus Oldcourses 2410 Docs Formulas Pdf


Www Cs Ubc Ca Arnaud Stat302 Cheatsheet Pdf



Stats Chapter 8



Poisson Distribution Probability With Formula P X Less Than Or Equal To K Youtube


Q Tbn And9gcrlhqgb0nmkf9opqbiv2phzg Ohrc0phczwr2pmbzcj0huiq0yh Usqp Cau


Http People Math Harvard Edu Knill Teaching Math464 1997 Math464 565 1997 Pdf



Solved A Discrete Random Variable X Has The Binomial Di Chegg Com



Stats Chapter 8


Arxiv Org Pdf 1309 3934



Formula Sheet Pdf Stat 333 Uwaterloo Studocu


Www Eit Lth Se Fileadmin Eit Courses Etsn10 Formula Sheet Pdf



Psyc 235 Introduction To Statistics Ppt Download


Http Www Math Cmu Edu Users Weikang Math325 Solhw6 Pdf


2



Pstat 5a 10 15 19 Swenson Studocu


Http Media News Health Ufl Edu Misc Bolt Intro Phc6050 6052 Unit3 0312unit3bbinomialrandomvariables Pdf



Ch2 Prob Supp424 Random Variable Mean



Several Probability Distributions Binomial Distribution And Poisson Distribution Programmer Sought



Chebyshev S Theorem Calculator


Http People Math Harvard Edu Knill Teaching Math464 1997 Math464 565 1997 Pdf


2



This Is Poisson S Distribution A Formulas For Your Comfort Facebook
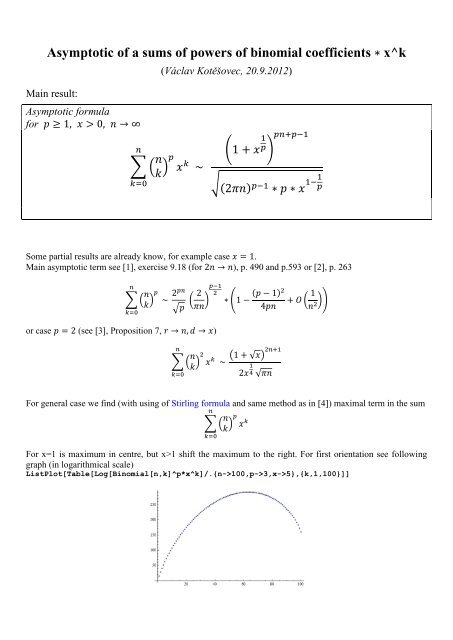


Asymptotic Of A Sums Of Powers Of Binomial Coefficients X K


Q Tbn And9gcrlhqgb0nmkf9opqbiv2phzg Ohrc0phczwr2pmbzcj0huiq0yh Usqp Cau



Hypergeometric Distribution Calculator



If 5 Is A Root Of The Quadratic Equation 2x2 Px 15 0 And The Quadratic Equation P X2 X K 0 Has Equal Roots Find The Value Of K Mathematics Topperlearning Com 1vxivscc


Fundamentals Of Probability Ppt Video Online Download


Http Pages Pomona Edu Ajr Fall08 Math58 Exams Math58fall08formulassheet Pdf



Poisson Distribution Probability With Formula P X Equals K Youtube



Solved Let X Be A Random Variable With P X K Ck For Chegg Com



Answered Chapter 5 Special Random Variables Bartleby


Order Statistics 10 30



Solved Problems Chapter Probability Review Pdf Free Download



Binomial Distribution Wikipedia



X Geom P And Q 1 P Derive The Formula E X 2 1 Q P 2 Hint To Compute This Course Hero


Http Www Tandfonline Com Doi Pdf 10 1080 08 Needaccess True



Hypergeometric Distribution Calculator
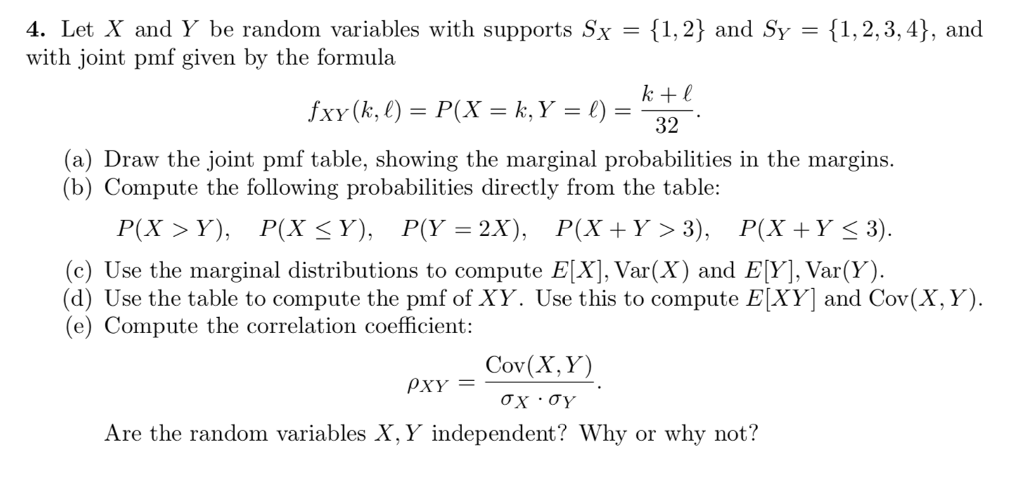


Solved 4 Let X And Y Be Random Variables With Supports S Chegg Com



Information Entropy A Study Of Unpredictability Boplet Agi


Yisun Io Teaching Autumn Stat251 Exams Prac Midterm Sol Pdf


2


2


Http Www Tandfonline Com Doi Pdf 10 1080 08 Needaccess True
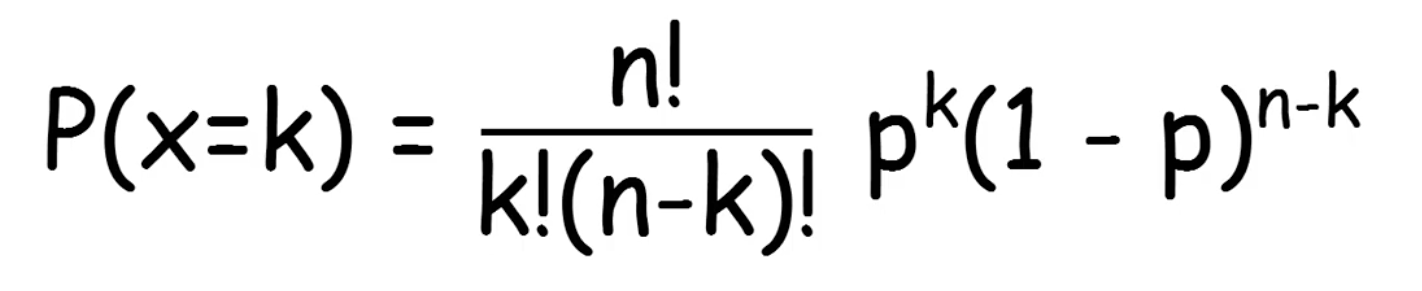


Day 60 Math Behind The Ml With Python 7 Probability By Samet Girgin Pursuitdata Medium
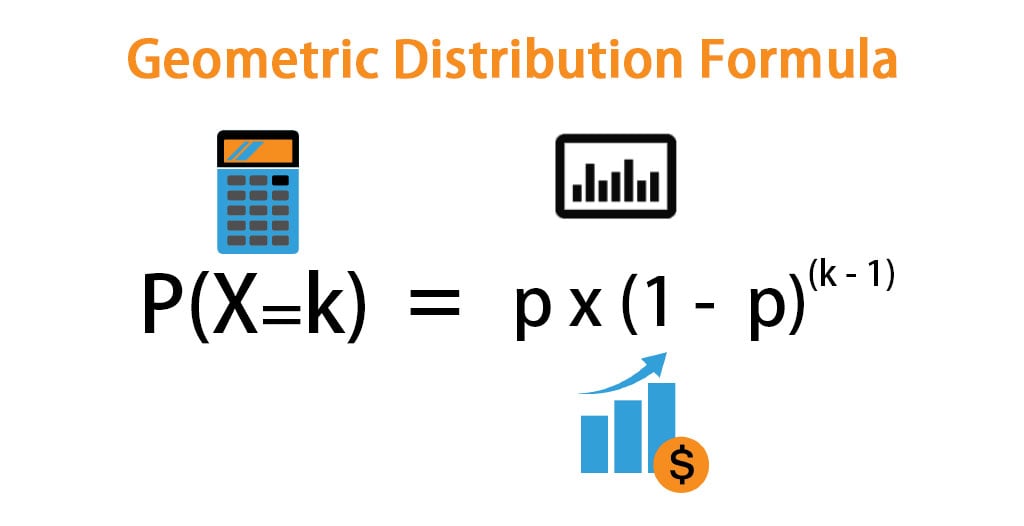


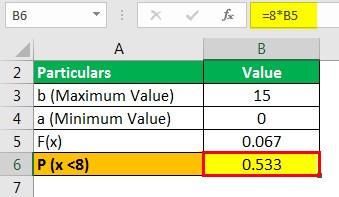
Geometric Distribution Formula Calculator With Excel Template


Http People Math Harvard Edu Knill Teaching Math464 1997 Math464 565 1997 Pdf



Assume That A Procedure Yields A Binomial Distribution With A Trial Repeated N 8 Times Homeworklib


Lesson 32 Exactly K Successes The Language Of Binomial Distribution Dataanalysisclassroom



Pdf On The Number Of Prime Factors Of An Integer


2


2



Answered Assume That A Procedure Yields A Bartleby


The Binomial Distribution



A Recursive Formula For Moments Of A Binomial Distribution



Ppt More Probability Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id



Cond Expec Exercises Ti2216m Studeersnel
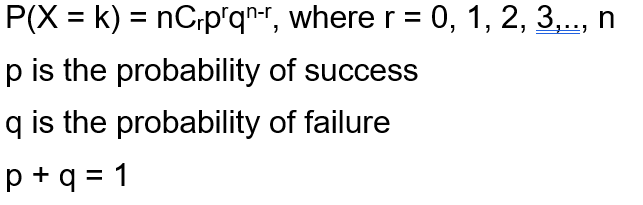


Binomial Distribution In R Programming Geeksforgeeks


コメント
コメントを投稿